
Too much body fat can harm health, as it is well known, but more and more evidence shows that the degree of harm to health in different parts of fat is not the same. The "orange peel wool" that is regarded as a vicious and affects beauty by women is actually a relatively harmless subcutaneous fat; as for the beer belly that is commonly seen in men, it is an internal fat that is very harmful to health, which may cause various chronic diseases, such as heart disease and fatty liver.
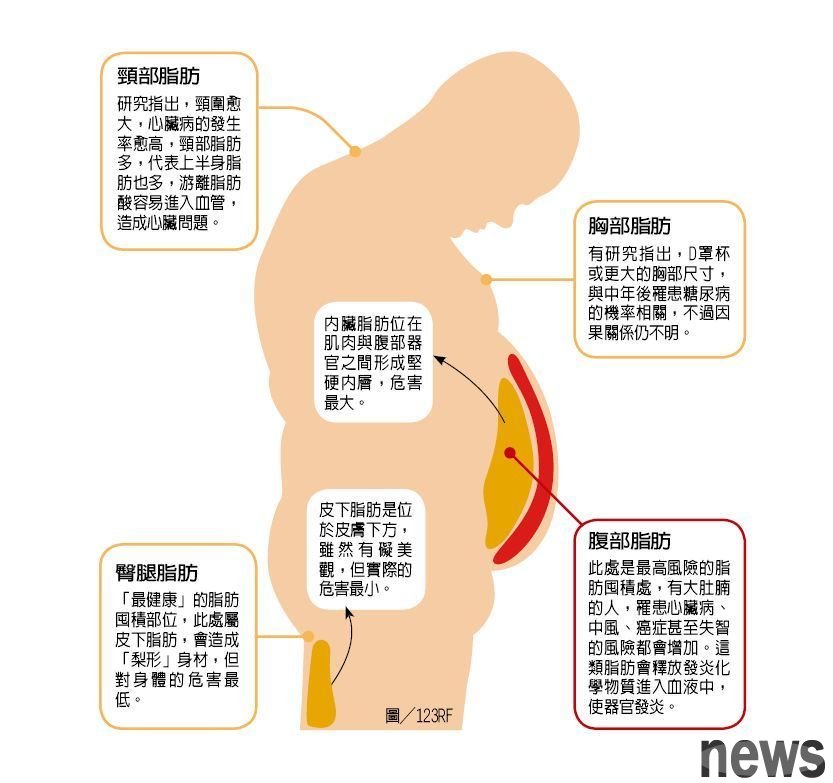
Subcutaneous fat is an unstable fat that is located under the skin, causing the fat group to form a dermis, and most of it is stored on the thighs and buttocks, forming the so-called "pear-shaped body". Although it has beautiful appearance, it has the least actual harm. Inner fat is usually the cause of beer belly, which is called "Apple-shaped body". This fat forms a hard inner layer between muscles and abdominal organs. It is generally believed that it will put chemical substances and hormones into the blood and cause inflammation.
A recent study summarized the risk difference between the two. Compared with subcutaneous fat, people with a high internal fat content have one-third more risk of heart failure. Researchers from the University of Texas have followed 2399 people aged 70 to 79 for 12 years and found that the fat in the muscles is inflammatory.
Hand and leg fat/threat to health★This is the most dangerous fat storage area for women, but in fact it is the least harmful subcutaneous fat. In addition to its location far away from important organs, studies have shown that compared with abdominal fat, fat stored in the legs has more than 100 genetic differences, making it less harmful.
A 2010 study pointed out that increasing weight in the lower body will cause more fat cells to be produced in the body; while obesity in the abdomen will cause fat cells to bloat. When the fat cells become too large, fatty acids will begin to leak into the blood, causing toxicity to the body.
Breast fat/threat to health★★★Large breasts may be a symbol of obesity, and obesity itself is a risk factor for many diseases. But in 2008, Harvard University conducted a study of more than 90,000 women in their 20s found that D-cup women are three times more likely to develop diabetes in middle age than A-cup women, even if their BMI is in normal range. Another 2012 study pointed out that larger breasts may represent more dangerous internal fats in these women.
The threat of vein fat/to health★★★★studies show that the larger the vein, the higher the risk of heart disease. The fat in the vein is more fat, which means that the upper body is also more fat, which causes the fatty acids to enter the blood and increases the risk of heart disease. Obesity in the cervix can also easily block the respiratory tract, affect sleep, hinder organ rest and regeneration, and increase heart pressure.
A recent study of "American Heart Health Magazine" found that compared with traditional indexes such as BMI, women have a 14-inch (35.56 cm) range and men have a higher risk of heart disease.
Abdominal fat/threat to health★★★★★★This is the most dangerous type of fat, which increases the risk of heart disease, medium wind, cancer, type 2 diabetes and dementia, because the fat here surrounds the important organs in the body. A 2019 study of 1.6 million women found that women with normal BMI (body quality index) but bulging abdomen (waist-hip ratio is higher than 0.85) have a 44% higher chance of death than women of similar age who have a fine waist. Their chances of heart disease and cancer are even higher than those with obese BMI values but relatively small abdomen.
Men are more likely to develop abdominal fat (beer belly) than women. It is generally believed that female estrogen can protect them from obesity far away from abdominals, and estrogen will store fat in the buttocks and thighs.
Once fat is stored in the body, it is impossible to lose weight on internal or subcutaneous fat. However, overall weight reduction and body fat reduction will help reduce the risk of the above diseases.
1. Research shows that more calcium and vitamin D content in the body is related to less internal fat. It is recommended to eat more dairy products such as green leaves, tofu, fish, egar and milk.
2. Converting fat and fat (mostly found in fatty red meat) into olive oil, peanuts, rapeseed oil, avocado and fruit can prevent fat accumulation in muscles.
3. A study pointed out that performing moderate exercises two to four times a week, at least 30 minutes at a time, can reduce the accumulation of internal fat by 7%, including brisk walking, single rides, aerobic exercise and strength training.
Next:What stole your time and freedom? Psychological counselor: Distracted behavior is an important signal to start procrastinating, and improving procrastination starts from two aspects