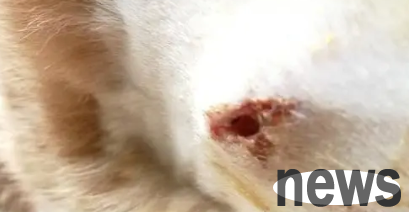
Cats are injured in wounds are easily invaded by bacteria, causing wound infection. Therefore, the wound needs to be cleaned and disinfected to prevent secondary infection of the wound. Generally, you can use normal saline to rinse the wound, clean foreign matter and impurities in the wound, and clean hair around the wound. This step requires fixing the cat to prevent the cat from struggling and scratching people. Then use iodine or alcohol to disinfect the wound. If the wound is large or there is suppuration fluid, it is recommended that the owner take the cat to medical treatment and a professional doctor will handle it. Because wounds may require suture or debridement, there is generally no suitable sterile environment at home, and secondary infection may occur by self-treatment.
To prevent cats from touching and scratching the wound again, they need to bandage the wound. First, use cotton to press the cat's wound to avoid exposure to the air. Use external anti-inflammatory drugs such as pet quick-coated to spray on the bandage and around the wound. Use tape to fix the bandage and cotton to prevent the cat from licking the wound. To prevent cats from scratching and tearing and bandaging the wound, the owner needs to wear an Elizabethan ring on the cat.